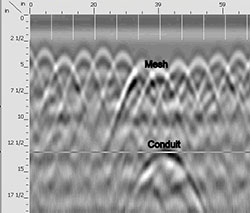
The radar method determines subsurface conditions by sending pulses of high frequency electromagnetic waves into the ground from a transmitter antenna located on the surface. Subsurface structures cause some of the wave energy to be reflected back to the surface, while the rest of the energy continues to penetrate deeper. The reflected wave energy is picked up by a receiver antenna on the surface. These signals are then processed and plotted in a distance-versus-time display. Thus, as the radar antenna is slowly towed across the surface, a continuous cross-sectional “picture” of subsurface conditions is generated.
GPR Applications
- Locate Pipes and Utilities
- Tank(UST) and drum location
- Concrete and Rebar Imaging
- Unmarked Cemetery and Grave Location
- Archaeological Studies
- Other Buried Objects